XJTU research team achieves breakthrough in small RNA profiling
The schematic diagram of ABC-seq technology principles.
Small RNA (sRNA) refers to a class of non-coding RNAs approximately 16-200 nucleotides (nt) in length, primarily including microRNA (miRNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), and small cytoplasmic RNA (scRNA).
Though sRNAs do not encode proteins, they play critical regulatory roles, particularly in post-transcriptional gene regulation.
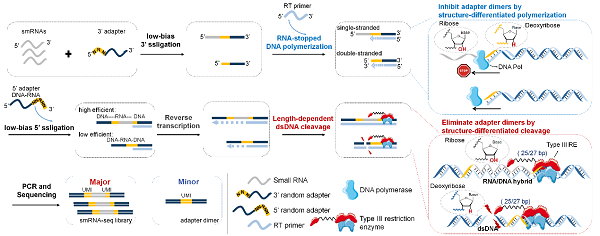
High-throughput sequencing is the key method for genome-wide discovery and analysis of sRNAs. Current sRNA sequencing techniques involve ligation or polymerization reactions to add universal adapters (5' and 3' adapters) to sRNA ends for library construction and uniform amplification and sequencing.
However, these methods face two major challenges: low reaction efficiency for rare sRNAs due to sequence bias and adapter dimer byproducts, which reduce usable sequencing data and compromise coverage/quantification accuracy by 30–50 percent.
A team led by Professor Zhao Yongxi at Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) has developed randomized adapter pool dimer blocking and cleavage in smRNA-seq (ABC-seq), which uses a randomized adapter pool to improve ligation efficiency and reduce bias, suppressing and cleaving adapter dimers to minimize byproducts.
Tested in tumor cell lines, cardiomyocytes, and clinical blood samples, ABC-seq demonstrated 9.4 percent higher miRNA detection in hypertrophic cardiomyocytes versus conventional methods and identified 172 therapy-responsive miRNAs in CD4+ T cells from non-small cell lung cancer patients, revealing immune-regulation mechanisms.
The technology has been patented in China and published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition under the title ABC-seq Expands Small RNAs Profiling with Successive Nucleic Acid Structure-differentiated Enzymatic Recognition.

